| [1] 朱卫东,孙志琴.龙血竭的药理作用研究[J].黑龙江医药, 2006, 19(5):403-404.
[2] 林芳,任杰红.血竭的药效学研究[J].云南中医中药杂志, 1999, 20(1):31-33.
[3] 锦亮,江东福.云南血竭的化学成分及抗真菌活性[J].云南植物研究,1995,17(3):336-340.
[4] 屠鹏飞,陶晶,胡迎庆.龙血竭黄酮类成分研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2003,1(1):27-29.
[5] 申秀民.广西血竭化学成分的研究[J].中草药,2004,35(7):728.
[6] 陈定芳,宋启示.血竭资源开发的研究进展[J].广州中医药大学学报,2004,21(6):489-492.
[7] 蓝鸣生.龙血竭研究进展[J].医学文选,2005,24(6):1053-1055.
[8] 徐淑卿,沙明,孟宪生.血竭的稳定性研究[J].中成药,2005,27(5): 598-601.
[9] 南莉莉,张超,杜娟,等.现代口服药物的吸收问题及促吸收方法的概述[J].上海医药,2008,29(8):355-358.
[10] Kawaguchi H.Functional polymer microspheres. Prog Polym Sci.2000;25:1171-1210.
[11] Ugelstad J,Berge A,Ellingsen T,et al.Preparation and application of new monosized polymer particles. Prog Polym Sci.1992;17:87-161.
[12] Uhlen M.Magnetic separation of DNA. Nature. 1989;340: 733-734.
[13] Rembaum A,Yen RGK,Kempner DH,et al.Cell labelling and magnetic separation by means of immunoreagents based on polyacrolein microspheres. J Immunol Methods.1982; 52: 341-351.
[14] Li X,Sun Z.Synthesis of magnetic polymer microspheres and application for immobilization of proteinase of balillus sublitis. J Appl Polym Sci.1995;58: 1991-1997.
[15] Ugelstad J,Søderberg L,Berge A,et al.Monodisperse polymer particles: a step forward for chromatography. Nature. 1983; 303:95-96.
[16] Xia Y,Gates B,Yin Y,et al.Monodispersed colloidal spheres: Old materials with new applications. Adv Mater. 2000;12: 693-713.
[17] Schärtl W.Crosslinked spherical nanoparticles with core-shell topology. Adv Mater. 2000;12:1899-1908.
[18] Caruso F. Nanoengineering of particle surfaces. Adv Mater. 2001; 13:11-22.
[19] 何卫东,潘才元.核壳聚合物粒子[J].功能高分子学报, 1997, 10(1): 110-117.
[20] 官建国,邓惠勇,王维,等.以胶体粒子为模板制备核壳纳米复合粒子[J].化学进展,2004,16(3):327-334.
[21] 乐园,陈建峰,汪文川.空心微球型纳米结构材料的制备及应用进展[J].化工进展,2004,23(6):595-599.
[22] Kumar V,Banker GS.Target-oriented Drug Delivery Systems[A].In: Banker GS. Rbodes CT eds. Modern Pharmaceutics. 3ed. NewYork: Mareel Dekker,1996:611-680.
[23] 陆彬.药剂学[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2003:437.
[24] 廖工铁.靶向给药制剂[M].成都:四川科学技术出版社,1997.
[25] 李凤前,胡晋红.肝靶向给药系统研究的新进展[J].中国药学杂志, 2002,37(5):321-325.
[26] 曹同玉,刘庆普,胡金生.聚合物乳液合成原理、性能及应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,1997.
[27] Kamiyama M,Koyama K,Matsuda H,et al.Micron-sized polymeric microsphere by suspension polymerization.J Appl Polym Sci.1993;50:107-113.
[28] 于涌,杨万泰.高交联反应性空心聚合物微球的制备及其表面吸附纳米银粒子的应用[D]. 北京化工大学博士学位论文,2007.
[29] 杨万泰,邢长民.一种马来酸酐与醋酸乙烯酯共聚反应的方法,专利号:ZL 200310115329.4.
[30] Xing CM,Yang WT.A Novel Facile Method for the Preparation of Uniform Reactive Maleic Anhydride/Vinyl Acetate Copolymer Micro- and Nanospheres. Macromol Rap Commun. 2004;25:1568-1574.
[31] Xing CM,Hong Y,Dong Y,et al.Novel Fluorescent Polymer Nanoparticles with Chemically Bonded Tetraphenylethylene Derivatives. 233rd ACS National Meeting, Division of Polymer Chemistry, USA,2007;48:466-467.
[32] Xing CM,Yu Y,Yang WT.Stabilizer-Free Dispersion Copolymerization of Maleic Anhydride and Vinyl Acetate. I. Effects of Principal Factors on Microspheres. J Polym Sci A. 2005;43:3760-3770.
[33] Xing CM,Yu Y,Yang WT.Stabilizer-Free Dispersion Copolymerization of Maleic Anhydride and Vinyl Acetate. II. Polymerization Features.Macromol Chem Phys. 2006;207(6): 621-626. |
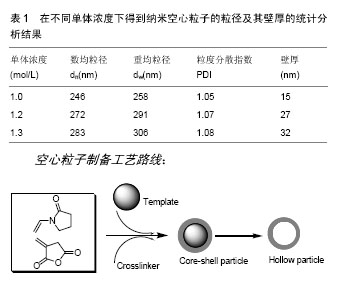
.jpg) 式中di为单个微球粒径;dn为微球数均粒径;dw为微球重均粒径;n为样本容量;PDI为粒径分布指数。
式中di为单个微球粒径;dn为微球数均粒径;dw为微球重均粒径;n为样本容量;PDI为粒径分布指数。